The simplest reason for a Windows computer frequently disconnecting from Wi-Fi Network could be due the computer not being set to automatically connect to Wi-Fi Network.
In such cases, the computer remains connected to Wi-Fi network as long as it is being actively used and tends to disconnect from the network, whenever it goes to sleep.
Apart from this, the problem of computer disconnecting from Wi-Fi can be caused due to the Network Adapter drivers becoming damaged or corrupted, the power supply to Network Adapter being switched OFF and other reasons.
Computer Keeps Disconnecting from Wi-Fi
If your computer is frequently disconnecting from Wi-Fi, start by restarting the computer to rule out the possibility of the problem being caused due to a stuck program or process.
If the problem still persists, you can follow other troubleshooting steps as provided below to fix the problem of Wi-Fi connectivity on your computer.
1. Set Computer to Automatically Connect to Wi-Fi Network
If your computer is disconnecting from Wi-Fi after every browsing session, the problem is most likely to the computer not being set to automatically connect to Wi-Fi.
1. Click on the Network Icon located in the Taskbar.
2. Select your Wi-Fi Network and make sure Connect Automatically option is selected and click on the Connect button.
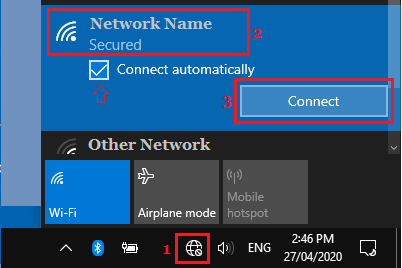
3. When prompted, enter your Wi-Fi Network Password and click on the Next button.
After this, you should hopefully find your computer consistently being connected to Wi-Fi network.
2. Install Updates
The problem might be due to a Windows update waiting to be installed on your computer.
1. Open Settings > scroll down and click on Windows Update in the left-pane. In the right-pane, click on the Check for Updates button.
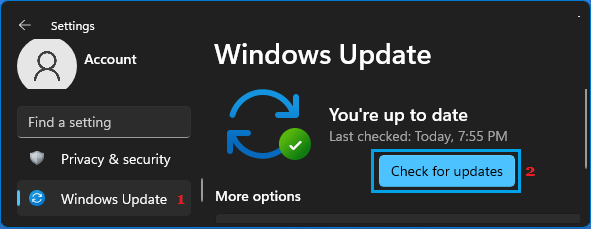
2. Allow Windows to check for available updates and download them on your computer.
3. Update Network Adapter Driver
As mentioned above, the problem could be due to drivers for the Network Adapter on your computer not being updated.
1. Right click on the Start button and click on Device Manager.
2. On Device Manger screen, expand Network Adapters > right-click on the Wi-Fi Adapter and click on Update Driver Software option.
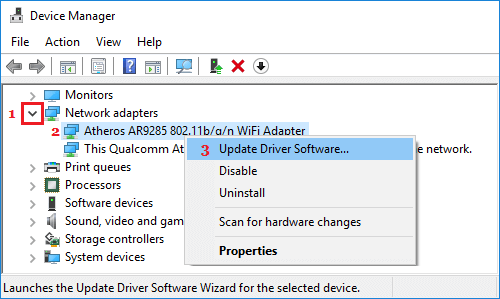
Tip: If you are not sure, look for something that has Network, 802.11b or Wi-Fi in it.
3. On the next screen, select Search automatically for updated driver software option and follow the instructions to install updated driver software (if available).
4. Run Network & Internet Troubleshooter
You can try the built-in Network & Internet Troubleshooter to find and fix Wi-Fi connectivity problem on your computer.
1. Go to Settings > System > scroll down in the right-pane and click on Troubleshoot. On the next screen, click on Other troubleshooters.
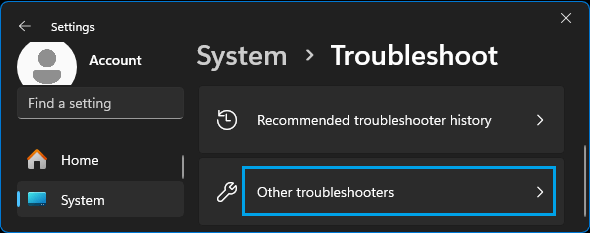
2. On the next screen, click on the Run button located in “Network & Internet” tab.
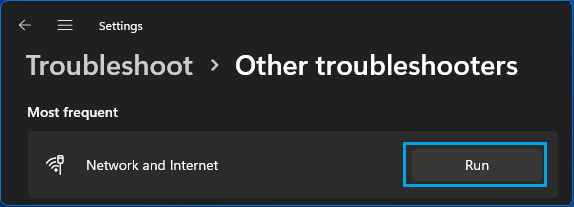
3. Follow onscreen instructions as the troubleshooter tries to find and fix internet connectivity problems on your device.
5. Stop Computer From Turning OFF Wi-Fi Adapter
As mentioned above, the problem could be due to the Network Adapter on your computer being automatically switched OFF to save battery life.
1. Right-click on Start button and click on Device Manager.
2. On Device Manger Screen, expand Network Adapters entry > right-click on the Network Adapter for your computer and click on Properties.
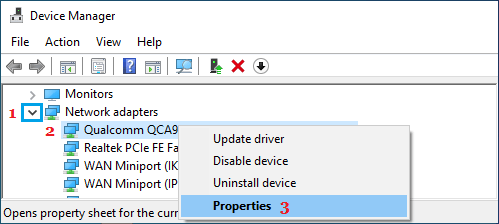
Note: If you see too many entries, look for something that says Network or 802.11b or has Wi-Fi in it.
3. On Wi-Fi Adapter Properties screen, switch to Power Management tab and uncheck Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power option.
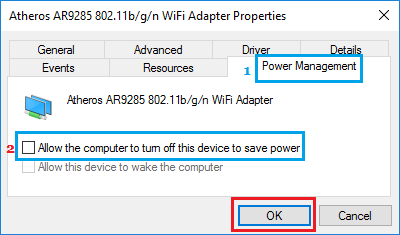
4. Click on OK to save this Power setting on your computer.
This stops the computer from switching OFF the power supply to the Wi-Fi Adapter, which in-turn prevents the Wi-Fi Network password from being erased.
6. Reset TCP/IP
1. Type CMD in the Search bar > right-click on Command Prompt in the search results and select Run as Administrator option.
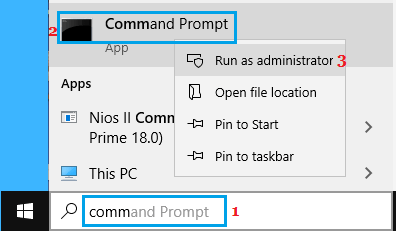
2. Type netsh winsock reset on the Command prompt screen and press the Enter key.
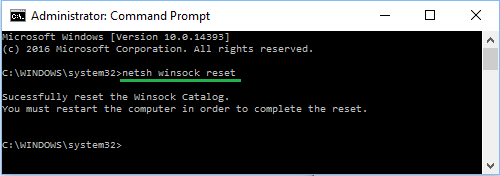
3. Similarly, type netsh int ip reset and press the Enter key
Close the Command Prompt window, Restart your computer and see if the problem is now fixed.
7. Disable Microsoft Wi-Fi Direct Virtual Adapter
The purpose of Microsoft Wi-Fi Direct Virtual Adapter is to support the sharing of internet connection on your computer with other devices (Hotspot).
If you are not using Hotspot, you can disable the Wi-Fi Direct Virtual adapter on your computer and see if this helps in fixing the Wi-Fi connectivity issue on your computer.
1. Right-click on the Start button and click on Device Manager.
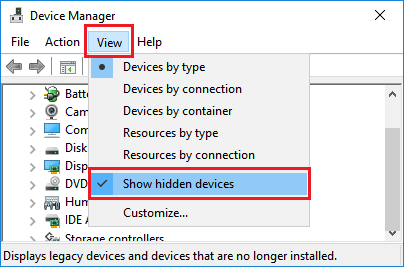
2. On the Device Manager screen, switch to View tab and select Show Hidden Devices option in the drop-down menu.
3. Next, right-click on Microsoft Wi-Fi Direct Virtual Adapter and click on Disable Device option.
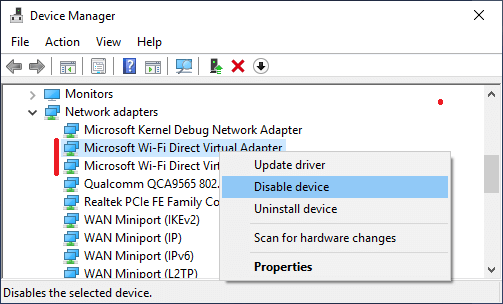
Note: After disabling Microsoft Wi-Fi Direct Virtual Adapter, you won’t be able to use Mobile Hotspot feature on your computer.
8. Set Low Roaming Sensitivity
Setting Low Roaming Sensitivity prevents the computer from constantly trying to connect to other available networks.
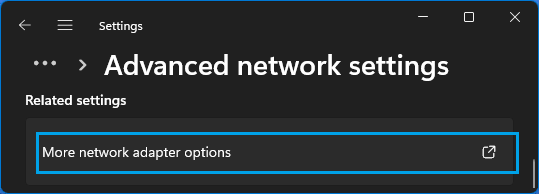
1. Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Advanced Network Settings > scroll down and click on More Network Adapter Options.
2. On the next screen, right-click on your Wi-Fi Network and click on Properties.
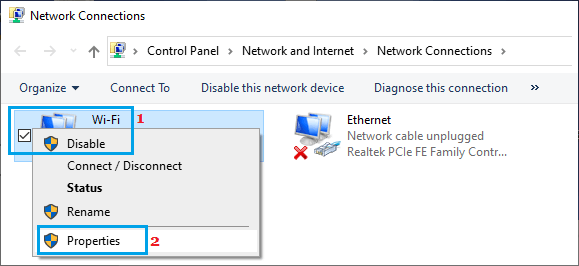
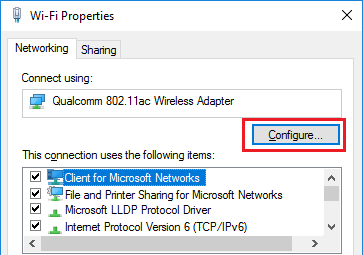
3. On Wi-Fi Properties screen, click on the Configure button.
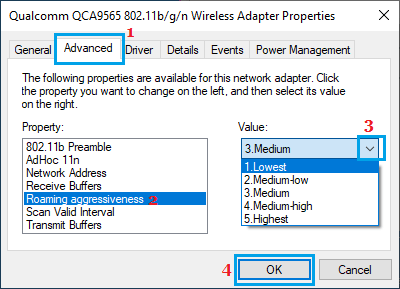
4. On the next screen, switch to Advanced tab and set Roaming Aggressiveness value to Lowest or Medium-low level.
Your computer will now have a lesser tendency to disconnect from Wi-Fi and try to connect to other networks.